Comparing B2B and B2C eCommerce: A Side-by-Side Analysis

Table of Contents
E-commerce continues to redefine how businesses operate globally. With the rise of digital-first strategies, both B2B and B2C eCommerce models are experiencing rapid evolution. While B2C e-commerce has popularized instant shopping experiences, B2B e-commerce is quietly dominating in terms of volume, value, and long-term growth potential. Understanding the core differences between B2B and B2C eCommerce, especially in terms of customer journeys, decision-making processes, platform requirements, and technological expectations, is crucial in the present competitive digital commerce landscape.
According to Statista, the global eCommerce market is projected to surpass $8.8 trillion in 2025, with B2B eCommerce accounting for nearly 80% of that value, emphasizing its dominance over the B2C segment.
The Present Landscape of B2B and B2C eCommerce
The landscape of digital commerce will have dramatically evolved by 2025. B2B eCommerce now leads the market, projected to hit $7.1 trillion in global sales by the end of 2025 (Statista), with a CAGR of 17.1%. In contrast, B2C eCommerce stands strong at $2.8 trillion, growing at a CAGR of 9.3%.
B2B eCommerce platforms have adopted AI-driven procurement tools, dynamic pricing models, and API integrations, enabling seamless and scalable transactions. Meanwhile, B2C platforms continue to thrive through personalization, mobile commerce, influencer marketing, and omnichannel experiences.
Both models face distinct challenges, from cart abandonment in B2C to complex procurement cycles in B2B, but each plays a crucial role in the digital economy.
Key Characteristics of B2B & B2C Models
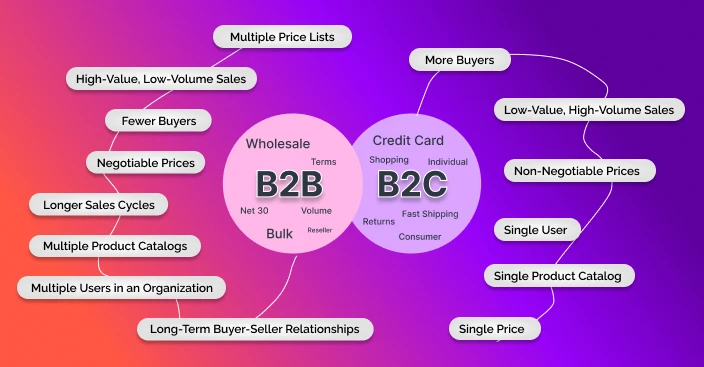
B2B
Fewer Buyers
B2B models typically involve fewer buyers than B2C models. B2B transactions are often between large companies rather than between individual consumers. This means that there are fewer potential customers for B2B businesses but that the value of each sale is typically much higher than in B2C transactions.
High-Value, Low-Volume Sales
B2B transactions are usually high-value, low-volume sales. This means that each sale is worth a significant amount of money but that the number of sales made is relatively low compared to B2C models. B2B sales are typically made to large organizations, which may only purchase a small number of products or services at a time.
Negotiable Prices
The prices of B2B transactions are often negotiable, whereas the prices of B2C transactions are typically non-negotiable. B2B sales are typically made between large organizations, which have the bargaining power to negotiate prices and terms with suppliers. In B2C transactions, on the other hand, the sellers set prices and are not open to negotiation.
Longer Sales Cycles
B2B sales cycles are typically much longer than B2C sales cycles. B2B transactions are often more complex and involve multiple decision-makers within the purchasing organization. The longer sales cycle also allows the seller more time to build a relationship with the buyer, which can increase the chances of making a sale. However, with AI-based CRM tools and automated procurement workflows, many businesses are now reducing lead times by up to 30%.
Long-Term Buyer-Seller Relationships
Long-term buyer-seller relationships are often characteristic of B2B transactions. B2B sales are typically made between large organizations, which need to build trust and establish a rapport with their suppliers to ensure a smooth and efficient supply chain. In B2C transactions, on the other hand, the focus is typically on making a one-time sale to an individual consumer.
Multiple Users in an Organization
In B2B models, multiple users within a single organization are often involved in the purchasing process. This can include procurement officers, finance managers, and technical specialists. This means that B2B sellers need to be able to communicate effectively with multiple stakeholders within the purchasing organization to close a sale.
Multiple Product Catalogs
B2B businesses often maintain multiple product catalogs, each tailored to the specific needs of a particular customer segment. This allows B2B sellers to offer their customers a more tailored and personalized experience and can help increase the chances of making a sale.
Multiple Price Lists
B2B businesses often maintain multiple price lists, each tailored to the specific needs of a particular customer segment. This allows B2B sellers to offer different prices to customers based on volume, payment terms, and other negotiated conditions.
B2C
More Buyers
B2C models typically involve a larger number of buyers than B2B models. B2C sales are made to individual consumers rather than large organizations. As a result, B2C businesses have a wider pool of potential customers and can reach a larger audience with their sales and marketing efforts. With the increasing popularity of mobile commerce and social commerce, businesses can reach up to 4.9 billion potential B2C users globally by 2026 (GSMA Intelligence) .
Low-Value, High-Volume Sales
B2C transactions are typically low-value, high-volume sales. This means that each sale is worth a relatively small amount of money, but the total number of sales made is much higher than in B2B transactions. B2C sales are made to individual consumers, who may make multiple purchases at a time.
Non-Negotiable Prices
The prices of B2C transactions are typically non-negotiable, whereas the prices of B2B transactions are often negotiable. B2C sales are made to individual consumers, who lack the bargaining power to negotiate prices and terms with suppliers. In B2B transactions, on the other hand, the prices are often negotiable, as large organizations have the bargaining power to negotiate with suppliers.
Single User
In B2C models, there is typically only one user involved in the purchasing process – the individual consumer. This means that B2C sellers need to be able to communicate effectively with individual consumers to close a sale. In B2B models, on the other hand, multiple users within a single organization are often involved in the purchasing process.
Single Product Catalog
B2C businesses typically have a single product catalog designed to meet the needs of all individual consumers. This enables B2C sellers to provide a consistent experience to all customers, making it easier to manage inventory and pricing. In B2B models, on the other hand, there are often multiple product catalogs, each designed for the specific needs of a particular customer segment.
Single Price
B2C businesses typically have a single price for each product, which is the same for all customers. This makes it easier for B2C sellers to manage pricing and ensures that all customers are charged the same amount for the same product. In B2B models, on the other hand, there are often multiple price lists, each tailored to the specific needs of a particular customer segment.
Differences Between B2B vs B2C Customers in eCommerce
While both models focus on selling customers’ products or services, there are several key differences between B2B and B2C customers. In this section, we will explore the differences between B2B vs B2C customers in e-commerce and discuss the impact these differences have on website design, pricing, payment, delivery, and checkout processes.
Buying Process (Timing)
One of the key differences between B2B and B2C customers is the timing of the buying process. B2B customers often take longer to make a purchase, as the buying process involves multiple decision-makers within a company. On the other hand, B2C customers tend to make purchases more quickly, as the buying process is typically limited to a single decision-maker. By 2025, B2B eCommerce platforms with AI-assisted buying journeys have seen a 24% reduction in sales cycle length (McKinsey, 2025).
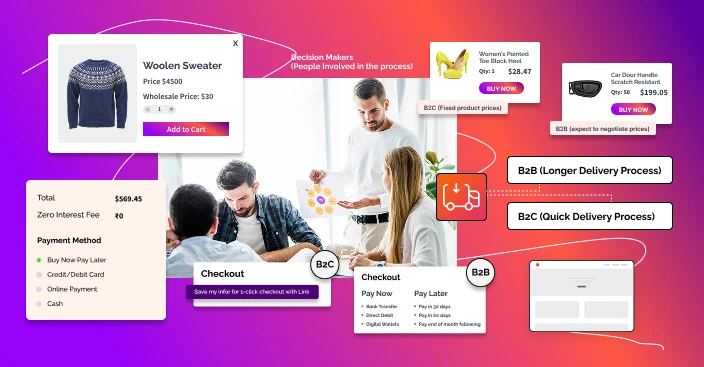
Decision Makers (People Involved in the process)
Another key difference between B2B and B2C customers is the number of decision-makers involved in purchasing. In B2B sales, multiple decision-makers are typically involved, including procurement, finance, and management teams. In B2C sales, on the other hand, the purchasing process is usually limited to a single decision-maker.
Relationship (Short or Long Term)
B2B and B2C customers also have relationships with e-commerce companies. For example, B2B eCommerce customers often have longer-term relationships with suppliers, as they typically make multiple purchases from the same supplier over time. B2C customers, on the other hand, tend to have shorter-term relationships with suppliers, as they typically make one-off purchases.
Pricing (Fixed or Tailored)
B2B and B2C customers also have different expectations when it comes to pricing. For example, B2C eCommerce customers typically expect fixed product prices as they make smaller purchases. On the other hand, B2B customers often expect to negotiate prices with suppliers as they make large purchases and have the bargaining power to do so.
Payment (Advance or In-Parts)
The payment process is another key difference between B2B and B2C customers. B2B customers often make advance payments, as they have established relationships with suppliers and can negotiate payment terms. B2C customers, on the other hand, typically make payments in parts, such as at the time of purchase or when a product is delivered.With the adoption of digital invoicing and blockchain-based payment systems, flexible payment models such as Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) are gaining traction even in B2B.
Delivery (Quick or Lengthy Process)
The delivery process is another key difference between B2B and B2C customers. B2B customers often expect a longer delivery process, as they make large purchases and need time to prepare for the delivery of goods. B2C customers, on the other hand, typically expect a quick delivery process, as they make smaller purchases and need products delivered quickly.
Checkout & Payment Process
The checkout and payment processes for B2B and B2C customers can also differ. For example, B2B customers often expect a more complex checkout process as they make larger purchases and need to negotiate payment terms. B2C customers, on the other hand, typically expect a more streamlined checkout process, as they make smaller purchases and need a quick and easy payment process.
Website Design & Content
In e-commerce, the design and content of a website play a critical role in attracting and retaining customers. Regarding the differences between B2B and B2C customers, it’s important to understand that their needs and motivations differ. For example, B2B websites often require a more complex navigational structure and detailed information about products and services to help businesses make informed purchasing decisions.
In contrast, B2C websites tend to have a simpler structure that focuses on attracting and enticing consumers to purchase through eye-catching visuals and compelling product descriptions. Additionally, B2C websites may prioritize user experiences, such as ease of use and intuitive navigation, to encourage customers to complete a purchase. B2B platforms are integrating PWA (Progressive Web App) designs for enterprise mobility, while B2C websites are evolving with hyper-personalized UX, driven by behavioral analytics.
Understanding these differences between B2B and B2C customers is essential for creating effective e-commerce websites that meet the unique needs of each type of customer.
Conclusion
When exploring the world of eCommerce, it’s important to understand the basics of what is B2B and B2C are and how they differ in terms of their target customers, purchasing processes, and platform requirements. B2B and B2C e-commerce models differ in several key aspects, including their target audiences, sales approaches, and overall customer experiences. For example, B2B e-commerce is focused on serving businesses with a focus on high-value, low-volume sales, and long-term buyer-seller relationships. B2C e-commerce, on the other hand, is geared toward serving individual consumers, focusing on low-value, high-volume sales and short-term transactions.
Understanding these differences is crucial for creating effective e-commerce strategies for businesses in either model. Whether through website design and content, payment options, or delivery methods, businesses must cater to their target audience’s unique needs and preferences to succeed in the ever-growing world of e-commerce. As we head into 2026, eCommerce will be driven by automation, AI/ML personalization, decentralized payment technologies, and zero-party data collection. Businesses must not only distinguish between B2B and B2C strategies but also continuously evolve their platforms to meet the next-gen digital buyer’s expectations.
FAQs
 Why do B2B sales cycles take longer than B2C?
Why do B2B sales cycles take longer than B2C?
B2B purchases often involve larger amounts, more complex products, and multiple decision-makers in a company. This naturally takes more time than a consumer buying something for personal use.
 Do B2B customers pay more than B2C customers?
Do B2B customers pay more than B2C customers?
Yes. B2B transactions are usually high-value but happen less often.In B2C, sales are smaller in value but happen more frequently.
 Which one has faster delivery — B2B or B2C?
Which one has faster delivery — B2B or B2C?
B2C usually B2C usually has faster delivery since it involves smaller orders going directly to the customer. B2B deliveries can take longer because of large volumes and complex logistics.
 How do websites for B2B and B2C differ?
How do websites for B2B and B2C differ?
B2B websites focus on detailed product info, bulk order features, and tools for managing large transactions. B2C websites focus more on visuals, simple navigation, and quick checkout to encourage instant purchases.
 Are payment options different in B2B and B2C?
Are payment options different in B2B and B2C?
Yes. B2B often allows flexible payment terms like paying in installments or after delivery. B2C payments are usually made in full at checkout.



